Math 1470: Partial Differential Equations Summer Term 2023
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Course Syllabus
Math 1470: Partial Differential Equations
Summer Term 2023 (2237)
Course Overview
A partial differential equation (PDE) is an equation relating an unknown function of more than one variable with some combinations of its partial derivatives. For example, if ![]()
![]()
![]() , then
, then
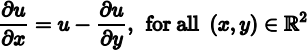
is a PDE.
The order of a PDE is that of the highest order derivative that appears in the equation. It is worth pointing out that the preponderance of differential equations arising in applications, in science, in engineering, and within mathematics itself, are of either first or second order, with the latter being by far the most prevalent. Third-order equations arise when modeling waves in dispersive media, e.g., water waves or plasma waves. Fourth order equations show up in elasticity, particularly plate and beam mechanics. Equations of order ![]() are very rare.
are very rare.
Typically, confronted with an equation like the one above, we ask ourselves questions like: Do functions ![]() satisfying this statement exist? If so, how many? What are their features? If you have taken a course on ordinary differential equations (ODEs), these issues should sound familiar to you. However, for reasons that we shall discuss, they are considerably more subtle in the PDE setting. Many things that you can take for granted with ODEs are just not true in general for PDEs.
satisfying this statement exist? If so, how many? What are their features? If you have taken a course on ordinary differential equations (ODEs), these issues should sound familiar to you. However, for reasons that we shall discuss, they are considerably more subtle in the PDE setting. Many things that you can take for granted with ODEs are just not true in general for PDEs.
In this course, we shall make a survey of the subject, beginning with the most basic equations and working our way up to some selected advanced topics. A (not-so-comprehensive) list follows.
Topics
first-order equations, method of characteristics, waves and diffusion, explicit solutions methods, Fourier series, PDEs in domains (boundary value problems), separation of variables, harmonic functions, Green’s functions, as well as some applications.
Course Goals
The goals of the course are that by the end of this course you will learn how PDEs arise in applications, what are some prototypical PDEs, and some of the fundamental concepts of PDE theory.
Students who completed Math 1470 are expected to fulfill the following Learning outcomes.
![]() Solve first-order PDEs using the method of characteristics.
Solve first-order PDEs using the method of characteristics.
![]() Solve some prototypical linear second-order PDEs using canonical variables for initial-value
Solve some prototypical linear second-order PDEs using canonical variables for initial-value
problems, Separation of Variables, and Fourier series for boundary value problems.
![]() Describe real-world systems using PDEs.
Describe real-world systems using PDEs.
Course Prerequisites
MATH 0240 (Calculus III) and one of MATH 0290 (Applied Differential Equations), MATH 1270 (Ordinary Differential Equations I). While I will review basic concepts from these courses, you are expected to be knowledgeable of their content.
Homework and LaTeX use
The only way to learn mathematics is to do mathematics! The majority of your learning will come through completing the homework assignments. These will be assigned weekly on Canvas and due Monday midnight. You are encouraged to work together on homework. However, each student must turn in his/her own assignments, and no copying from another student’s work is permitted. Also, please remember that the grader has to be able to follow your thought process in order to award credit. It is incumbent on you to ensure that your assignments are readable on a computer screen, both in terms of legibility and intelligibility.
Assignments completed in LaTeX, which is a standard mathematical typesetting package for science
and technology, will receive a 5% bonus. LaTeX![]() (https://www.latex-project.org/) is free and runs on all computers. You could either download it to your computer, or use the free web version Overleaf
(https://www.latex-project.org/) is free and runs on all computers. You could either download it to your computer, or use the free web version Overleaf ![]() (https://www.overleaf.com/) .
(https://www.overleaf.com/) .
Exams
There will be one midterm exam as well as a cumulative final. The midterm exam will be either in- class or take-home on Monday, June 5. The final exam will be on Thursday, June 22.
You are not allowed to collaborate/communicate with other students in any way during the exam or consult online repositories such as Chegg.com. Cheating on exams will be treated in accord with Academic Integrity Policy outlined below.
Grades
Your final grade will be determined according to the following formula:
Homework: 30%
Midterm: 30%
Final: 40%
Disability Resource Services
If you have a disability for which you are or may be requesting an accommodation, you are encouraged to contact both your instructor and the Office of Disability Resources and Services (DRS) as early as possible in the term; every effort will be made to accommodate your needs.
2023-05-23