ECON7560 Globalisation and Economic Development Practice Semester 1, 2022 Problem Set
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON7560 Globalisation and Economic Development
Practice Problem Set - Sample Answers
Semester 1, 2022
Q1 Name a country where GNI may be a better measure of economic well being than GDP? Why?
Answer: Lebanon, for example, receives a large value of remittances, related to its GDP. Gross National Income, which includes remittances, may better measure the economic resources available to its people than GDP does.
Q2 For each of the following statements, is it correct or not? Why?
(a) In the equation Y = C+I+G +NX, which decomposes GDP, G represents gross investment.
Answer: Incorrect. G represents government spendings on goods and services.
(b) Commodities and goods could be moved across countries while services could not. That’s the only reason why prices of commodities and goods are very similar across countries while the prices of services are not.
(c) Answer: Incorrect. Services could also be traded across national borders. For example, financial services and IT services. There are many other factors that contribute to the price differences of services. For example, trade policies and domestic laws and regulations may limit the trade of services.
Q3 Which empirical method does the following graph employ?
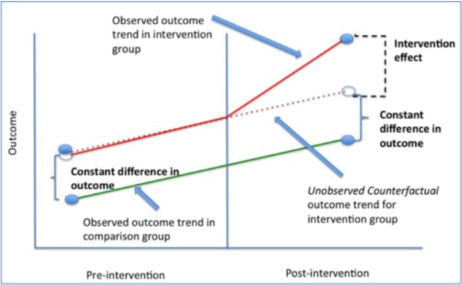
(a) Regression Discontinuity Design
(b) Difference in Differences <-
(c) Instrumental Variable Method
(d) Randomized Controlled Trial (e) Dynamic Clearing
(f) Don’t Ask, Don’t Tell
Q4 Suppose the ratio of 90-10 percentiles for income is 3.14 for the economy of Kangaroo Land, which of the following may possibly be the ratio of 80-20 percentiles for income in the same economy. Tick all that apply.
(a) 3.41
(b) 3.59
(c) 2.22
(d) 5.11 (e) 4.31
![]() 1.96
1.96
Answer: According to the definition of percentiles, any number that is smaller than 3.14 and greater than 1.
Q5 Suppose in a Solow model, we have the following parameter values: n = 0, s = 0.5, α = 0. 3. There is no growth in the total factor productivity so that At = A = 1. Moreover, we know that at time 0, the economy is at a steady state so that k* = k0 =1. Now imagine that a foreign power invaded this country. 1% of the population was killed and another 14% of the population fleeded the country to avoid violence. Moreover, 15% of capital stocks were destroyed. All of this happens in period t=1.
After that, the war ended and there was no more destruction of capital or loss of population (but the refugee permanently settled outside of the country and will never return. What is the growth rate of per-capita output in period t =4?
Answer: Both the aggregate capital stock and the population decreased by 15%. So it happens that there is no change in per-capita capital stock. Since there is no change in TFP, the output per capita is unchanged and the economy remains at its steady state. Therefore, in any period after t=0, there is no growth in output per capita because capital per capita is unchanged and TFP is constant.
2023-04-21