ECON 121 Growth
ECON 121 Growth
Professor Gu
Here is your final exam information:
Zoom link: see canvas—zoom.
Time: June 10 Thursday, 12pm-1:45pm (Pacific time), try to arrive at zoom 5mins earlier to prepare. We will all start together on zoom, and you can ask clarification questions if there are any during the exam. If no question, you can also sign off zoom and submit the answers back to Canvas whenever you finish before the due time.
It is your responsibility to make sure the submission is complete and on time. Points will be deducted for any incomplete submission.
Your exam will become available at 12pm PST on Canvas—Assignment, refresh your browser if we do not see the exam on the webpage right away.
Please explicitly write your answers for each question on a blank paper or on a word file; once you finish, scan/photo the answer sheets to a pdf or doc format and upload it to Canvas—Assignment—Quiz.
THIS IS AN OPEN-BOOK EXAM, SHOW YOU INDEPENDENT WORK. You must finish your exam by 1:45pm and complete submission by 2pm (Canvas can track your submission time), except for DRC students—please submit when you are done via Canvas—Assignment—Quiz if you still can, if not, please email the TA your answer sheets.
TEN short answer questions with subquestions, some numerical and some analytical. Cover contents of Ch1-16 (excluding Ch11, and for Ch6 up to where the lecture stopped).
Prep Materials:
Previous midterms, Practice questions below, TA sessions, Lecture questions, Problem sets, All Textbook post-chapter problems (including many those that are not assigned as homework, solutions are on Canvas--Modules), know/can derive formulas.
Key concepts/numbers:
Top 3 largest economies in terms of total GDP and population
Rule of 72
Productivity, technology, efficiency
Cobb-Douglas Production function and its assumptions and implications
Possible sources of differences in output per worker
Physical capital’s share of income
Solow growth model: both numerical and graphical
Solow growth model with growth dispersion
The relation between savings and income and income growth
Income trap
Current world population, US population
Malthusian model and its breakdown
Solow growth model with population growth: both numerical and graphical
Factors that affect population growth: life expectancy and fertility rate
Replacement fertility rate
Net rate of reproduction and its implication to population growth
Tempo effect
Demographic momentum
Growth rate of working-age fraction
Human capital measurements: Health measurement and Skill/education measurement
How health interacts with income in the model
Return-to-education: average annual return numbers and accumulative return calculation
Payments to human capital, payments to raw labor
Why higher wage premium to skilled/educated workers
Solow growth model with human capital: both numerical and graphical
Productivity and its components technology and efficiency: A=T*E
Possible sources of productivity differences
Role of productivity in determining output and output growth: 53% of cross-country income per capita difference is explained by productivity differences
Role of factor accumulation in determining output and output growth: 68% of cross-country income growth difference is explained by productivity differences.
Output = productivity x factors of production
Output growth = productivity growth + factor growth
Types of tech progress
Creative destruction
Patent system, US patent system
Alternatives to patent
One-country technology innovation model and when share of R&D workers increases (both graphical and numerical)
Two-country technology innovation/imitation model and steady state, and when share of R&D workers increases (both graphical and numerical)
Capital-biased tech change
When did the Industrial Revolution in Britain begin
Why did US have lower productivity during 1970s-1980s
Technology diffusion
Effects of past inventions on possible new inventions, fishing-out effect
Growth with differential tech progress
Moore’s law
Why did coal mining industry experience lower efficiency in 1970s
Types of inefficiency
How to determine the efficient allocation of labor between two sectors (both graphical and numerical)
What happens to labor allocation when average output is paid as wage, instead of MPL=wage (both graphical and numerical)
Why do countries have governments
How does government affect economic growth
Effect of corporate tax
Effect of labor income tax
Labor supply elasticity and its interaction with the effect of labor income tax
Corruption, democracy
Gini coefficient, Lorenz Curve
Kuznets Curve
Sources of income inequality
How does education affect income inequality
Effects of inequality on growth
Effect of inequality on tax
Median voter
Income mobility
Consumption inequality
Simultaneous Determination of Income and Culture Modernization
Renewable natural resource carrying capacity
Maximum sustainable yield
Great having y’all, and best luck to your finals!
Practice Questions
(See TA session for solutions)
1) In a certain country over some period of time, the annual growth rates of output per worker, physical capital per worker, human capital per worker, and technology were as follows:
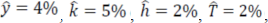
Assume that the production function is y = Ak2αh1-α, where the value of α is 1/3. What was the growth rate of efficiency?
2) In a certain country, 2/3 of the population has an income of zero, and the rest of 1/3 has income of exactly $100 each. What is the Gini coefficient in this country?
3) Suppose in this country, 10% of women died before reaching their reproductive age, for those who are able to live to bear children each of them gives birth to 4 kids on average, out of which half are baby girls. Solve for net rate of reproduction (NRR).
4) According to the average return to education we learnt in class, what is the ratio of the wage for completing 13 years of schooling relative to no-schooling?
5) Consider a country in which there are two sectors, called Sector 1 and Sector 2. The production functions in the two sectors are:
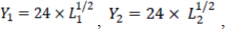
Workers in both sectors are paid their marginal products. The total number of workers in the economy is L=L1+L2=20.
A worker can only work in sector 1 if s/he pays a cost of X, which can be considered as education cost. Write the equation that can be used to solve the number of people who will end up working in sector 1 (i.e. the value of L1) as a function of X. This will be a nasty looking equation, and you should not attempt to solve it.
6) In lake A, the only kind of fish is catfish. The equation below describes the rate at which the fish grows without human intervention:
catfish: g=s*(80-s)/10
a) Calculate the optimal stock of catfish.
b) Calculate the maximum sustainable yield.
c) What is the carrying capacity for catfish?
7) If income inequality decreases in the economy, how would the uniform tax rate change according to the median voter model?
2021-06-10