ECON239: Development Economics Assignment #1
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
ECON239: Development Economics
Assignment #1 —— Detailed Answer Guide
February 22, 2023
Section A: Questions involving calculations.
Q1: The average annual growth rate is calculated as
1
g = (1 + G) T 二 1
where G denotes the overall growth and T is the time period. In this case, we have
1
g = (1 + 2) 15 二 1 = 0:0760
Q5: The cost of US basket in the US is (2 × 1000) + (10 × 2) = $2; 020:
The cost of the US basket in Kenya is (2 × 100000) + (10 × 50) = $200; 500:
It follows that the implied PPP exchange rate is $1 = K99:26:
Q6: The world basket of goods is 2.1 iPhones and 16 hamburgers.
The cost of world basket in the US is (2:1 × 1000) + (16 × 2) = $2; 132:
The cost of the US basket in Kenya is (2:1 × 100000) + (16 × 50) = $210; 800: It follows that the implied PPP exchange rate is $1 = K98:87:
Q7: The coordinates of the Lorenz curve are
|
Cum. pop. share |
0.25 |
0.50 |
0.75 |
1.00 |
|
Cum. inc. share |
0.05 |
0.15 |
0.40 |
1.00 |
The area under the curve plotted in Figure 1 can be computed as
S = (0:5 × 0:25) +0:25 × (0:05 + 0:15 + 0:4) = 0:275
![]() 尸
尸 一 尸 一
triangles rectangles
The Gini coe¢ cient is equal to the fraction of the area of the triangle below the line of equality ( ![]() ) that is covered by the area above the Lorenz curve:
) that is covered by the area above the Lorenz curve:
Gini = ![]()
![]()
S = 1 二 2S
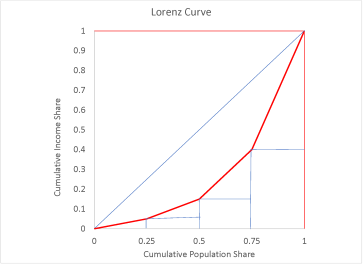
Figure 1: Question Q7
It follows that the Gini coe¢ cient is 0.45.
Q14: The steady state capital stock per worker satisÖes the equation
1
sAk 3 = (n + 6)k
Solving for k we get
k* = ╱ ![]() 、
、![]()
which in this case is
3
k* = 4 2 = 8
The steady state output per worker is then
1 1
y = Ak 3 = 3 × 8 3 = 6:
Section B: Mutipart Questions involving calculations.
B2. Household fertility choice
Q25: The budget constraint can be written as
C = 40(100 二 10N) 二 700N + 6000
![]()
![]()
![]() which simpliÖes to
which simpliÖes to
C = 10000 二 1100N:
Q26: If the household acts optimally, it will try to choose a point on its budget constraint. If at that point C = 5600, then the optimal number of children must satisfy
5600 = 10000 二 1100N:
It follows that N* = 4:
Q27: The budget constraint can now be written as
C = 40(100 二 10N) 二 700N + 7500
which simpliÖes to
C = 11500 二 1100N:
Q28: In this case, the optimal number of children must satisfy
6000 = 11500 二 1100N:
It follows that N* = 5:
Q29: The budget constraint can now be written as
C = 50(100 二 10N) 二 700N + 6000
C = 11000 二 1200N
Q30: In this case, the optimal number of children must satisfy
7400 = 11000 二 1200N:
It follows that N* = 3:
B3. Solow growth model
Q32: Initial capital per worker is simply
k0 = ![]() =
= ![]() = 10:
= 10:
Initial output per worker is then
![]() 1
1
Q33: The steady state capital per worker is given by
k* = ╱ ![]() 、2 = ╱
、2 = ╱ ![]() 、2 = 1:
、2 = 1:
The steady state output per worker is then
1
y* = A (k* ) 2 = 1:
Q35: The steady state capital per e§ective worker is given by
ke(*) = ╱ ![]() 、2 = ╱
、2 = ╱ ![]() 、2 = 0:327:
、2 = 0:327:
The steady state output per e§ective worker is then
1 1
ye(*) = (ke(*)) 2 = (0:327) 2 = 0:571:
Q37: The steady state capital per worker is given by
k* = h ╱ ![]() 、2 = 2 ╱
、2 = 2 ╱ ![]() 、2 = 2:
、2 = 2:
The steady state output per worker is then
1 1 1 1
y* = (h) 2 (k* ) 2 = (2) 2 (2) 2 = 2:
Q38: The steady state capital per worker is given by
k* = h ╱ ![]() 、2 = 4 ╱
、2 = 4 ╱ ![]() 、2 = 2:
、2 = 2:
The steady state output per worker is then
1 1
y* = (4) 2 (4) 2 = 4:
2023-03-08