CHEM 232 Exam 2 Review Worksheet
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
CHEM 232 Exam 2 Review Worksheet
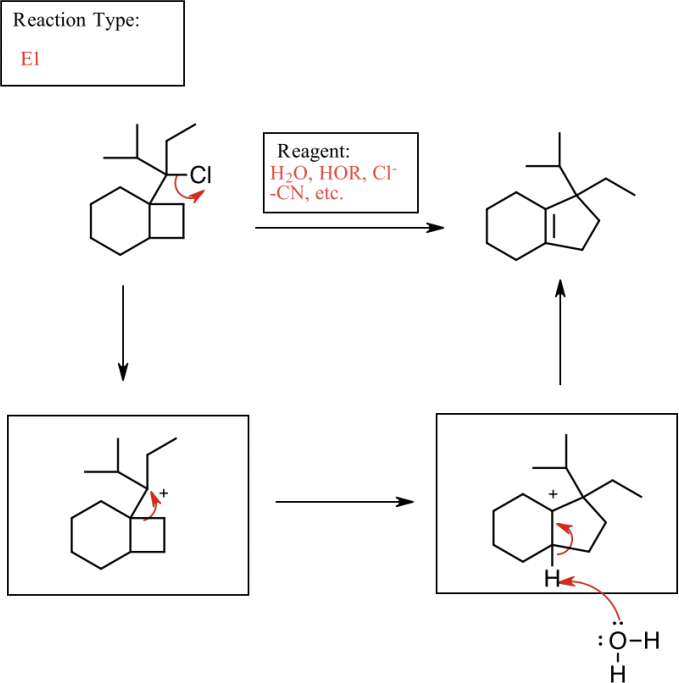
1. Draw a reagent that could be used to transform the alkyl halide into the final product on the right. Then, draw the arrow-pushing mechanism for the reaction. Indicate which type of reaction was used (SN2, SN1, E1, or E2).
2. Complete the table for the radical bromination reaction shown below
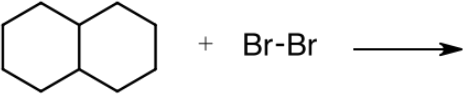
|
Position |
2° Carbons |
3° Carbons |
|
Statistical (# of H atoms) |
16 |
2 |
|
Experimental Product Distribution (give answer as %) |
29% |
71% |
|
Selectivity |
1 |
20 |
3. How will the rate of the following reaction change if:

a. the amount of nucleophile is halved
No change - nucleophile is not part of the rate equation for SN1 reactions
b. The solvent is changed from DMSO to acetic acid (CH3COOH)
Rate increases - SN1 is sped up by polar protic solvents because the carbocation is stabilized by hydrogen bonding
(hint: first determine what type of reaction is taking place)
4. Rank the following alkenes from most to least stable
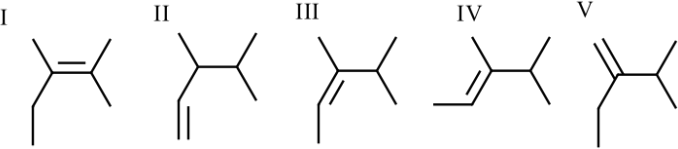
I, IV, III, V, II
a. If the molecule shown below is the starting material, which alkene will form if following Zaitzev’s rule during an E2 reaction? Draw a base that could be used for Zaitzev’s rule.

I
Potential Bases: good nucleophile strong base
Ex: NaOH, NaOCH3, LiNH2, etc.
b. If the molecule shown below is the starting material, which alkene will form if following Hofmann’s rule during an E2 reaction? Draw a base that could be used for Hofmann’s rule.

V
Potential Bases: poor nucleophile strong base
Ex: t-butoxide or LDA
5. Complete the table by filling in all known nucleophiles and bases in the proper quadrant and label each quadrant with the potential mechanisms that can occur.
|
|
Good Nucleophile |
Poor Nucleophile |
|
Strong Base |
|
|
|
Weak Base |
|
|
6. Draw the structure of the major elimination product given the two bases
a. Hydroxide (⁻OH)

b. Water (H2O)

7. Fill in the table denoting the dominant mechanism of each combination of electrophile and nucleophile. Then, use the table to predict the dominant mechanism in each scenario.
|
|
Poor Nu Weak Base |
Good Nu Weak Base |
Small Nu Strong Base |
Bulky Nu Strong Base |
|
Methyl |
No rxn |
SN2 |
SN2 |
SN2 |
|
1º unhindered |
No rxn |
SN2 |
SN2 |
E2 |
|
1º branched |
No rxn |
3º - SN2 4º - No rxn |
3º - E2 4º - No rxn |
3º - E2 4º - No rxn |
|
2º |
SN1/E1 |
SN2 |
E2 |
E2 |
|
3º |
SN1/E1 |
SN1/E1 |
E2 |
E2 |


![]() .
.
No rxn because no good LG
b. 
SN1/E1 because tertiary alpha and poor Nu/weak base
c. 
E2, Zaitzev because small strong base and secondary alpha C

![]()

![]() .
.
No rxn because alpha primary and beta fully substituted
8. Select the structure of the final product.

|
a. |
|
b |
. |
|
c. |
|
![]() .
.

a. Carbon chain sub wrong
b. Wrong stereochem
c. SN1 product (C+ rearrangement)
d. Correct
2023-03-01






