ETC3410 Practice Exam
ETC3410 Practice Exam
INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
• Answer ALL questions.
• Statistical tables are located at the end of this exam paper.
(For the practice exam, statistical tables are available on Moodle as a separate PDF file.)
Question 1 (30 marks)
1. A researcher studied the effects of potential experience on being a union member with the 1988 Current Population Survey data (“union.csv”). Variables in the data are as follows.
All the relevant variables are included in “union.csv” under the same variable names as described above.
(a) What is linear probability model? Briefly explain in words. (2 marks)
(b) The researcher wanted to estimate the logit model
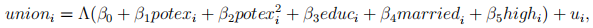
How would you run logit estimation for the above model with R? Write down the required R commands. (You do not need to use robust standard errors.)
In addition, write down the expression of marginal effects of having one more year of potential experience for a non-married individual who works in highly unionized industry with 10 years of education and two years of potential experience. Consider potex a continuous regressor. (5 marks)
(c) The researcher obtained the following output for the logit model in (1):
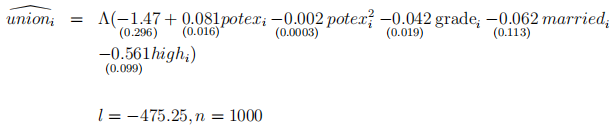
where l is the value of log-likelihood, and standard errors are in parentheses. Use the infor-mation in (2), to answer the following questions.
i) Calculate the value of marginal effects in part (b). Use e = 2.7. (3 marks)
ii) Test the following hypotheses at 5% level of significance:
. Clearly specify the test statistic, its distribution under the null hypothesis, the critical value of the test statistic, the rejection rule for the test and your conclusion. (4 marks)
(d) The researcher wished to test the following hypotheses at the same time.
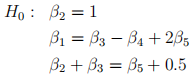
i) Write down the above hypotheses in the form of
. Clearly specify
. (3 marks)
ii) Briefly explain “Wald Test” in words. (3 marks)
(e) The researcher also wanted to test the following hypotheses using the likelihood ratio test.
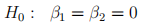
i) Write down the restricted (logit) model to implement the LR test for the above hypotheses. (3 marks).
ii) What is the distribution (and the degree of freedom if applicable) of the LR test statistic when the researcher test the above hypotheses? (2 marks)
2. State if each of the following statements is true or false, and BRIEFLY give your reasoning.
(a) The maximized value of the log-likelihood for the restricted model is less than or equal to that for the unrestricted model. (2 marks)
(b) The Wald test statistic W is equivalent to
, where q is the number of restrictions in the null hypotheses and LR is the corresponding likelihood-ratio test statistic for the same test. (3 marks)
Question 2 (40 marks)
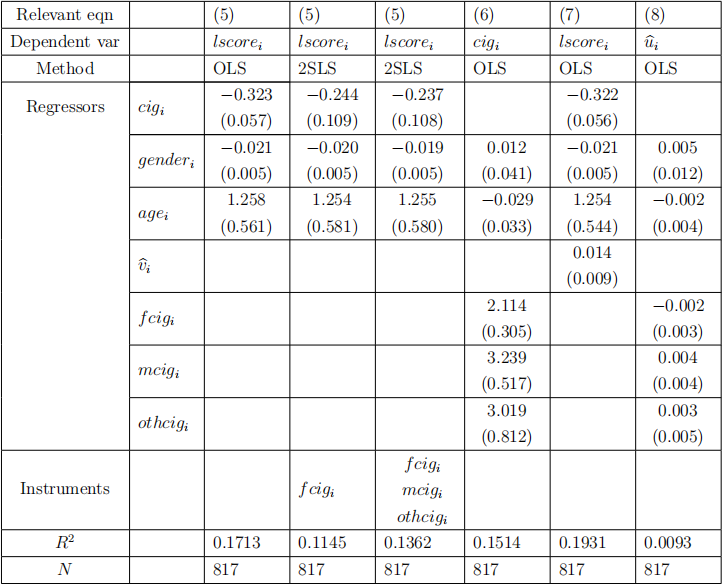
1. An econometrician wants to investigate the effects of smoking on exam scores of university students. The researcher collected a dataset (“univ.csv”) including the following variables
All the relevant variables are included in “univ.csv” under the same variable names as described above.
He estimated the following equation,
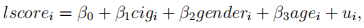
by using OLS.
He is advised that students who have low exam scores may smoke more due to stress on grades. So, he also estimated the equation (5) using simple IV with f cigi as an instrumental variable for cigi, and 2SLS using fcigi, mcigi, othcigi as a set of instrumental variables for cigi.
He also estimated the following equation as the first stage using OLS:
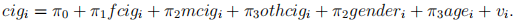
Finally, he estimated two extra equations using OLS:
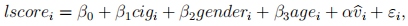
and
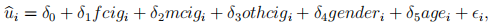
where
is the residual from OLS estimation of (6), and
is the residual from 2SLS estimation of (5) using f cigi , mcigi , othcigi as a set of instrumental variables.
The estimation results are as follows
Using the information provided above, answer the following questions.
(a) Write down all required R commands that carry out the 2SLS estimation together with its first-stage result using f cigi , mcigi , othcigi as a set of instrumental variables for cigi . (2 marks)
(b) From the equation (5), answer the following question. What happens to the individual’s test score, if an individual smokes two more cigarettes per day, ceteris paribus. (2 marks)
(c) By using 2SLS regression results, where f cigi is the only instrumental variable outside of the equation (5), test the following hypotheses at 5% level of significance:
vs.
. Clearly specify the test statistic, its distribution under the null hypothesis, the critical value of the test statistic, the rejection rule for the test and your conclusion. (4 marks)
(d) Test if the three instrumental variables f cigi , mcigi , and othcigi are jointly exogenous at 1% level of significance. Clearly specify the test statistic, its distribution under the null hypothesis, the critical value of the test statistic, the rejection rule for the test and your conclusion. (4 marks)
(e) Test if cigi is endogenous at 10% level of significance. Clearly specify the test statistic, its distribution under the null hypothesis, the critical value of the test statistic, the rejection rule for the test and your conclusion. (4 marks)
2. Let the structural equations be
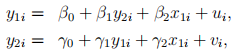
where u and v are independent.
(a) Write down the reduced form equation for y2i. (3 marks)
(b) Suppose
. What is the identification status of the first equation (y1 equation)? Explain. How about the second equation (y2 equation)? Explain. (3 marks)
(c) Suppose
. What is the identification status of the first equation (y1 equation)? Explain. How about the second equation (y2 equation)? Explain. (3 marks)
(d) Suppose
. What is the identification status of the first equation (y1 equation)? Explain. How about the second equation (y2 equation)? Explain. (3 marks)
3. Let
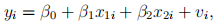
where 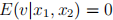 . However, we do not observe
. However, we do not observe 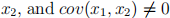 . We have a variable w outside of the equation (9).
. We have a variable w outside of the equation (9).
(a) Write down conditions under which the variable w is a valid instrumental variable so that you can consistently estimate β1. (3 marks)
(b) Write down conditions under which the variable w is a valid proxy variable so that you can consistently estimate β1. (3 marks)
4. Consider a simultaneous equations model of supply and demand. You observe variables of equilibrium price, equilibrium quantity for each observation (a product). You have a variable “aggregate real income” for each observation.
(a) Suppose “aggregate real income” is a demand shifter but not a supply shifter. Is either of supply and demand equation identified? If yes, which one? Explain. (3 marks)
(b) Suppose “aggregate real income” affects both demand and supply equation. Is either of supply and demand equation identified? If yes, which one? Explain. (3 marks)
Question 3 (30 marks)
1. There is a great deal of discussion and disagreement about the most effective way to reduce crime. In particular, participants in the debate disagree about the relative importance of detection, punishment, and social and economic conditions in influencing crime rates. We use a panel data set to investigate this issue. For the purpose of this investigation, we interpret the variables lpa and lpc as measures of the probability of detection, lpp and las as measures of the severity of punishment, and lwage as a crude measure of economic conditions. Of course, there are many other unobserved factors that influence crime rates.
Consider an unobserved effects model of the crime rate given by
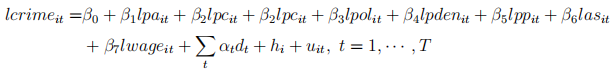
where T = 3.
(a) Under what condition(s) on hi and/or uit, is FE estimation more appropriate than RE estimation? Explain. (3 marks)
(b) Suppose RE is more appropriate than FE. That is, the condition(s) in part (a) does not hold. Is RE estimator unbiased for β? Explain. How about POLS? Explain. (4 marks)
(c) Now, suppose fixed effects model is more appropriate. If you use FE estimation, can you estimate coefficients on the time dummies dt for all t? Explain. (4 marks)
Now, suppose that lpa does not change over time.
(d) Can you estimate β1 with RE? How about with POLS? Explain. (3 marks)
(e) Write down the modified equation that allows you to estimate annual changes in the marginal effects of lpa from year 1 to years 2 and 3. (4 marks)
2. State if each of the following statements is true or false, and BRIEFLY give your reasoning.
(a) Suppose that strict exogeneity and cross-sectional independence hold, and
. If
, then both POLS and RE are efficient. (3 marks)
(b) One can use the Hausman test to choose between the RE and the POLS estimators for estimating the unobserved effects model. (3 marks)
(c) The standard errors for the FE estimator and the FD estimator are exactly the same if T, the time dimension of the corresponding panel dataset, is two. (3 marks)
(d) If the unobserved effects model includes a regressor
, or age-squared, the coefficient on
cannot be estimated in first difference estimation. (3 marks)
END OF EXAMINATION
2021-05-27