COMPSCI 1103, 2103 Algorithm Design and Data Structures 2
Primary Examination, Semester 2, 2017
COMPSCI 1103, 2103
Algorithm Design and Data Structures

Instructions
• Begin each answer on a new page in the answer book.
• Examination material must not be removed from the examination room.
Materials
• Foreign language paper dictionaries permitted.
DO NOT COMMENCE WRITING UNTIL INSTRUCTED TO DO SO
Programming Fundamentals
Question 1
(a) What does the following code snippet print out?
int a = 5;int b = 7;int * c = &acout << a << ", " << b << endl;*c = 9;cout << a << ", " << b << endl;c = &b;*c = 1;cout << a << ", " << b << endl;
[3 marks]
(b) Read the following code snippet and identify the problem with it.
int a[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};for (int i = 0; i <= 5; i++){cout << *(a + i) << endl;}
[2 marks]
(c) Declare and initialise (to zero) a two-dimensional array of floats on the heap. Please provide the corresponding C++ code.
[3 marks]
(d) Explain the difference between: Pass by Value, Pass by Pointer, Pass by Reference when declaring C++ functions. Give an example of each and explain how they work.
[3 marks]
(e) List three differences between the following two memory areas:
• The Stack
• The Heap
[3 marks]
(f) What will the following code snippet print out? Explain your answer.
int a;cout << a << endl;
[2 marks]
(g) One strategy for developing algorithms is a Greedy approach. Explain what defines an algorithm as “greedy” and give an example of an al-gorithm that employs a greedy strategy.
[3 marks]
[Total for Question 1: 19 marks]
Inheritance and Object Oriented Programming
Question 2
(a) What is an abstract class? Explain how to create an abstract class and what consequences it has for object creation.
[2 marks]
(b) What is the difference between the keywords private and protected?
[2 marks]
(c) Please clearly describe, in the context of C++, the difference between:
• redefining
• overloading
• overriding
You may use diagrams where necessary.
[4 marks]
(d) What does the friend keyword do? Explain how to use the friend keyword and what it allows.
[2 marks]
(e) Consider the following code snippet.
int compare(int a, int b){return a > b;}
Write C++ code to declare a function pointer and direct it to use function compare.
[2 marks]
(f) A game programmer decides to make a game called block-jumper. There are three kinds of objects in the game: The player, enemies & blocks. Each object has an x & y location, and a function draw which takes two parameters (x & y). The programmer decides to create a parent class called GameEntity.
i. Draw a class diagram showing all four classes, the functions, vari-ables and inheritance relationships.
[4 marks]
ii. The player has three health points. The enemies have a gold value (given to the player when killed) and an attack function. Update your class diagrams to reflect these changes.
[3 marks]
[Total for Question 2: 19 marks]
Recursion
Question 3
(a) What are the three conditions necessary for controlled recursion?
[3 marks]
(b) Consider the mathematical expression:
1 + 3 + 5 + 7 + · · · + (2n − 1) = n2
Using recursion write a function that calculates n2 for a given n using the left-hand side of the above expression.
[4 marks]
(c) What is tail recursion? Explain how it works and what problem tail recursion helps mitigate.
[2 marks]
(d) What is Dynamic Programming? Explain how it differs from normal recursion and what the main benefit is.
[3 marks]
[Total for Question 3: 12 marks]
Complexity Notation
Question 4
(a) What is the definition of f(n) being in O(g(n))?
[1 mark]
(b) What is the definition of f(n) being in Ω(g(n))?
[1 mark]
(c) Please prove that 2n3 + 5n2 + 100000 is in Θ(n3).
[4 marks]
(d) Please prove that n2 + 60 is not in O(n).
[1 mark]
(e) Given that f(n) ∈ O(n2) and g(n) ∈ O(n log n), please formally prove that f(n) + g(n) ∈ O(n2).
[4 marks]
(f) We know that kn is in O(n) for any constant k. Is the following claim correct? Briefly explain.
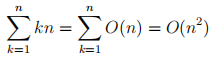
[3 marks]
[Total for Question 4: 14 marks]
Sorting and Searching
Question 5
(a) Please illustrate the process of sorting the list {2, 8, 6, 1, 9} using bub-ble sort.
[2 marks]
(b) Please illustrate the process of merging the two sorted lists {2, 3, 6, 8} and {1, 2, 9, 12} using mergesort.
[2 marks]
(c) i. Given a list of n integers, you are asked to sort them in ascend-ing order using quicksort. Please write down the pseudo-code of quicksort with the last element as pivot. You must give the details of the partitioning process.
[5 marks]
ii. The performance of quicksort depends on the selection of the pivot value. What is the best-case performance of quicksort?
[1 mark]
iii. What kind of pivot value will result in the best-case performance? Please provide some analysis.
[2 marks]
iv. What kind of pivot value will result in the worst-case performance? Please provide some analysis.
[2 marks]
(d) Describe bucket sort for a list of int using pseudo-code.
[4 marks]
(e) Given that sorting a large dataset is often time-consuming, is it a good idea to sort before searching?
[2 marks]
(f) Consider the following modified version of binary search: Let L be a list of sorted values and let n be the number of elements in L:
• Check L[n/3] and L[2n/3]
• The above value determines which sublist to focus on (it should be noted that there are three sublists with size n/3)
• Run the same algorithm recursively on the sublist
Please write down the pseudo code for this algorithm and analysis the computational complexity.
[6 marks]
[Total for Question 5: 26 marks]
Linked Lists
Question 6
Define a linked list containing n nodes as follows:
struct Node {int data;Node *link;}
(a) Please describe how to swap two adjacent elements by adjusting only the links (and not the data) using:
i. Singly linked lists
[2 marks]
ii. doubly linked lists
[2 marks]
(b) In a singly linked list, each node only has link to the next node. What does the following function do? Please analyse the complexity of the function.
void print(Node *head){if(!head)return;print(head -> link);std::cout << head -> data << std::endl;}
[4 marks]
(c) Stacks and Queues are often implemented based on linked lists.
i. What is a stack and what are the common operations?
[3 marks]
ii. What are the common operations of the Queue ADT?
[2 marks]
iii. Please give an application of the stack.
[2 marks]
(d) A deque is a data structure consisting of a list of items, on which the following operations are possible:
• push(x): Insert item x on the front end of the deque.
• pop(): Remove the front item from the deque and return it.
• inject(x): Insert item x on the rear end of the deque.
• eject(): Remove the rear item from the deque and return it.
How do you use the singly linked list to implement a deque which support the basic operations above to be done with O(1) complexity?
Please provide C++ code segments and analysis to support your de-sign.
[8 marks]
[Total for Question 6: 23 marks]
Trees
Question 7
Define a tree node as follows:
struct Node {int data;Node *left;Node *right;}
(a) What is a binary search tree?
[1 mark]
(b) Starting with an empty tree, show the process of adding the list {3, 6, 1, 2, 5, 4} (in order) to the tree.
[3 marks]
(c) Write a function bool search(struct Node *root, int obj) that takes as input a binary search tree root and a value of obj. The function re-turns whether obj exists in the tree or not.
[3 marks]
[Total for Question 7: 7 marks]
End of exam
2021-05-25