MAST20004 Probability Semester 2 Assessment, 2019
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Semester 2 Assessment, 2019
MAST20004 Probability
Question 1
(1) Let A, B ∈ Ω be two events.
(1-i) Argue carefully to show that
B = (A ∩ B) U (B/A)
and
A U B = A U (B/A).
(1-ii) Use the finite additivity property for probability to show that
P(A U B) = P(A) + P(B) 一 P(A ∩ B).
(1-iii) Suppose that A and B are independent, and AUB = Ω . Show that P(A) = 1 or P(B) = 1.
(2) Suppose that we roll a fair die twice. Consider the following three events:
A : the sum of the two values is 7,
B : the first die rolls a 3,
C : the second die rolls a 4.
(2-i) Describe the sample space associated with the underlying random experiment. (2-ii) Show that the above three events are pairwisely independent.
(2-iii) Are they mutually independent?
Question 2
(1) Suppose that there are two baskets of fruit. The first basket contains 6 apples and 4 ba- nanas. The second basket contains 3 apples and 7 bananas. A person first chooses one of the two baskets with equal probability, and then chooses an item from it uniformly at random.
(1-i) What is the probability that the person obtains a banana?
(1-ii) Given that the person obtains a banana, what is the conditional probability that the banana comes from the second basket?
(2) A security device will erroneously refuse 1 in 2000 authorised persons to enter the building of a company. The device will erroneously admit 1 in 100, 000 unauthorised persons. Suppose that 90 percent of those who seek access to the building are authorised. If a person is refused entry to the building by the security device, what is the probability that the person is indeed authorised?
Question 3
(1) Let X be a continuous random variable whose probability density function is given by
![]() , 2
, 2
(0, otherwise.
(1-i) Find the cumulative distribution function of X .
(1-ii) Compute the mean and variance of X .
(2) Let Y be uniformly distributed over the interval [一2, 3]. Compute the probability den- sity function of Y2 .
Question 4
Let
D = {(x, y) ∈ R2 : x2 + y2 < 1, y > 0}
be the upper half unit disk in the x-y plane. Suppose that (X, Y) is a bivariate random variable whose joint probability density function is given by
, 2
fx﹐Y(x, y) = . π , (0,
(x, y) ∈ D,
otherwise.
(i) Compute P(Y > |X|).
(ii) Compute the marginal probability density functions of X and Y .
(iii) Compute E[X] and E[Y].
(iv) Let (R, Θ) be the polar coordinates of (X, Y). Compute the joint probability density func- tion of (R, Θ).
(v) Are R and Θ independent? Justify your answer.
Question 5
Let (X, Y) be a bivariate random variable whose joint probability density function is given by
fx﹐Y(x, y) = ![]()
(i) Find the value of C .
(ii) For y ∈ (0, 1), compute the conditional probability density function of X given Y = y . (iii) Compute E[X|Y].
(iv) By conditioning on Y , use the law of total expectation to compute E[X].
Question 6
Let (X, Y) be a bivariate normal random variable with parameters
µx = 1, µY = 一1, σx(2) = 4, σY(2) = 9, ρ = 一 ![]() .
.
(i) Compute P(|X| > 2).
(ii) Compute P ╱X < ![]() |Y = 2、.
|Y = 2、.
(iii) Let U = X + Y and V = 7X 一 2Y . Compute Cov(U, V).
(iv) Are U and V independent? Justify your answer.
[Recall that the joint probability density function of a general bivariate normal random variable
(X, Y) ![]() N2(µx, µY , σx(2), σY(2), ρ) is given by
N2(µx, µY , σx(2), σY(2), ρ) is given by
fx﹐Y(x, y)
= 2πσxσY1^1 一 ρ2 exp ╱ 一 2(1 1一 ρ2 ) ╱ (x 一σµ2xx)2 一 2ρ(x 一 ![]() 一 µY ) + (y 一σµ2YY )2 ←← .]
一 µY ) + (y 一σµ2YY )2 ←← .]
Question 7
Suppose that the number of calls that a company receives on Monday morning is a Poisson random variable X with parameter 8.
(i) What is the probability that the company receives more than 2 calls on Monday morn- ing?
(ii) Suppose that the number of calls that the company receives on Monday afternoon is a Poisson random variable Y with parameter 10. Assume that morning calls and afternoon calls are independent. What is the distribution of the number of calls that the company receives on Monday? Justify your answer.
(iii) Suppose that the number of calls that the company receives throughout a year is a Poisson random variable Z with parameter 6000. How do you approximate P(Z > 6000)? Explain the reason behind your method.
Question 8
Consider the game of rolling a fair die. If it rolls a “2” or “4”, you will be awarded $1. If it rolls a “6”, you will be awarded $4. If it rolls an odd number, you will not receive any award.
(i) Find the mean and variance of your award in an individual game.
(ii) Suppose that you roll the die repeatedly and independently for 100 times. Use the central limit theorem to approximate the probability that your total award will be greater than $90.
Question 9
Suppose that the error of measuring the velocity of a molecule in some gas is a continuous random variable X whose probability density function is given by
fx(x) = e-2|α| , 一& < x < &.
(i) Find the moment generating function of X .
(ii) Use the moment generating function to compute E[X] and Var[X].
(iii) By computing the moment generating function of |X|, show that |X| ![]() exp(2).
exp(2).
Question 10
A child is playing the game of jumping among the vertices of a square and its centre (see the figure below where the centre and the vertices of the square are labelled for your convenience).
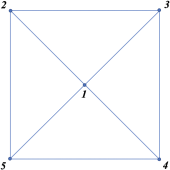
If the child is currently at the centre, in the next move he/she either remains at the centre with probability α, or jumps to one of the four vertices with equal probabilities. If the child is currently at one vertex, in the next move he/she either jumps to the centre with probability α, or jumps to one of the two neighbouring vertices with equal probabilities. Here 0 < α < 1 is a fixed parameter. Suppose that initially the child is at the centre of the square. Let {Xn : n ≥ 0} be the Markov chain recording the position of the child at each move.
(i) Write down the one-step transition probability matrix for {Xn : n ≥ 0}.
(ii) Find the probability that, after n moves the child returns to the centre of the square. (iii) For which value(s) of α can we see that
π = ╱ ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ,
, ![]() ←
←
is the equilibrium distribution of {Xn : n ≥ 0}?
(iv) For general α, by making some symmetry considerations, find the equilibrium distribution of {Xn : n ≥ 0}.
2023-02-01