Intro Math Modeling (MATH-UA 251) Spring 2022
Hello, dear friend, you can consult us at any time if you have any questions, add WeChat: daixieit
Intro Math Modeling (MATH-UA 251)
Spring 2022
Homework 2
Please give complete, well-written solutions to the following exercise. Provide sufficient jus- tification and explanation for a classmate who has not worked on the exercise to understand your solution.
Spherical Coordinates: The spherical coordinate system uses a distance r from the origin along with two angles θ and φ to uniquely locate a point in space. An elemental volume in spherical coordinates is illustrated below:
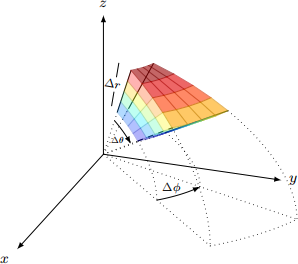
The radial distance r is measured from the origin; the angle φ( [0, 2π) varies in the xy plane and is zero on the x axis; the angle θ( [0, π] measures the deviation from the z axis. The projected radius onto the xy plane is r sin(θ). The radii of curvature for angles θ and φ are r and r sin(θ), respectively. Therefore, we have the following formula for the volume of the element, V , and area in different directions (treating the elemental volume as a rectangular box for small ∆r, ∆θ, ∆φ):

Here, Ar , A9 , Ao denote the area in the r, θ, φ directions.
Exercise 1. [50 pts] The mass flux (mass per unit area per unit time) can be expressed as

where ρ is density of the material and u is the vector of velocity with scalar components ur , u9 , uo in r, θ, φ directions, respectively.
Write a shell balance for the elemental volume to derive the differential form of the continuity equation in spherical coordinates. Next, simplify your answer for constant ρ .
Exercise 2. [50 pts] The heat flux (thermal energy per unit area per unit time) can be expressed as

where the new parameters Cp , k, T are the specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity, and temperature, respectively, and the gradient operator in spherical coordinates is

Write a shell balance (with a heat source s) for the elemental volume to derive the differential form of the heat equation in spherical coordinates. Next, simplify your answer for constant ρ, Cp , k .
2022-02-15